Have you seen the black and white, square, pixelated images in payment gateways, restaurant menus, or business cards?
Ever wondered what they are?
You might have heard the term 'QR Code' and wondered what it stands for or how it works.
You’re new to the world of QR Codes or want to learn more about them.
This article has all your answers.
Table of contents
- What is a QR Code?
- A brief history of QR Codes
- The purpose of QR Codes
- The different parts of a QR Code
- How does a QR Code work?
- How to scan a QR Code?
- How to create a QR Code?
- Are QR Codes safe?
- The different types of QR Codes
- Who should use QR Codes?
- Where to use QR Codes?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a QR Code?
A QR Code stands for Quick Response Code. It is a two-dimensional barcode that stores information easily accessible with a scan. You can scan them with a QR Code scanner or a QR Code reader (nowadays available on all mobile phones).
You can store any type of data in a QR Code: URL addresses (single or multiple), text, images, PDFs, phone numbers, SMS, email, and more.
QR Codes: a brief history
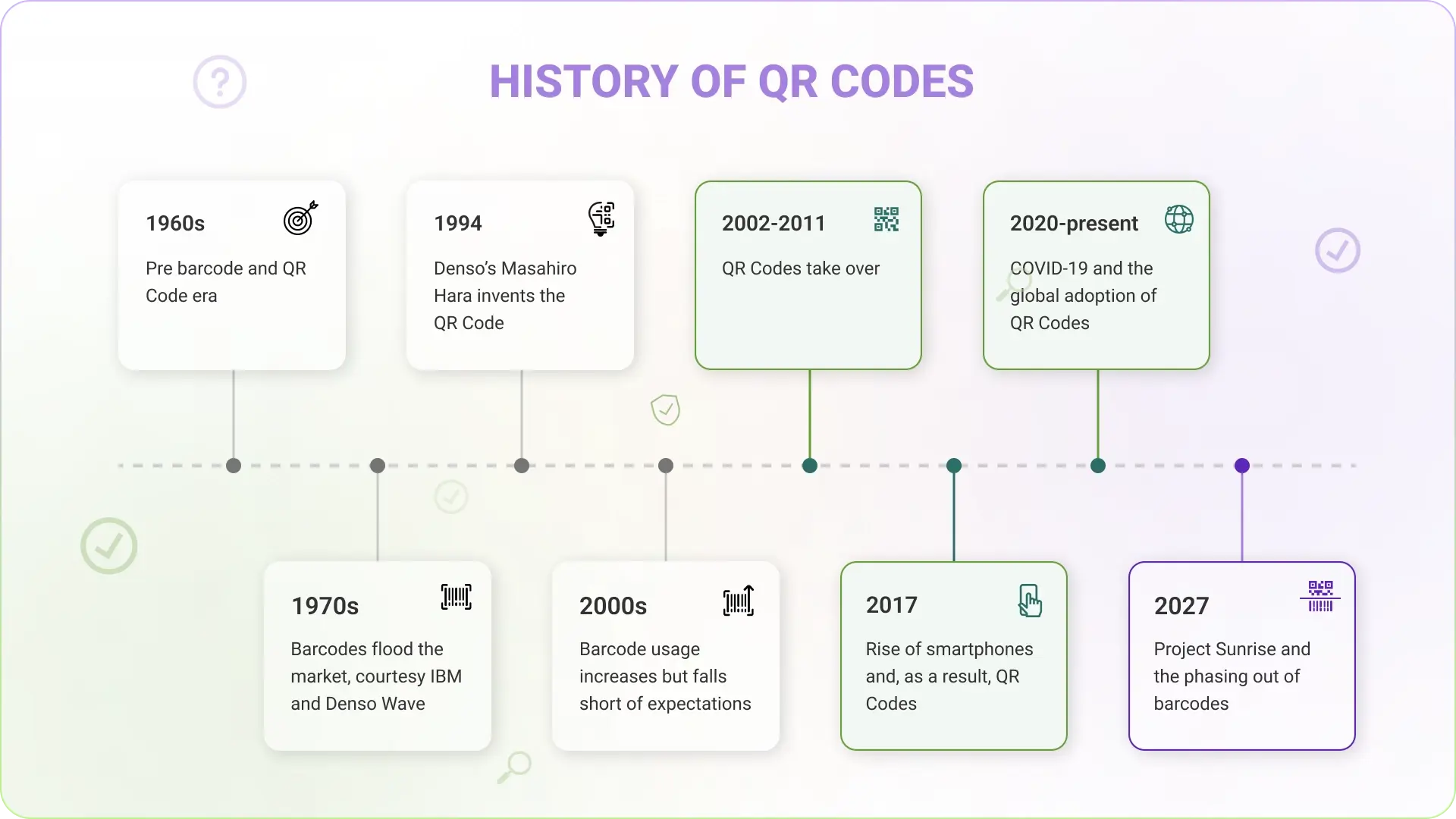
QR Codes have a fascinating history that can be traced back to 1994. Masahiro Hara and the Denso Wave team invented a better version of barcodes: QR Codes.
Bar codes were one-dimensional and could only be scanned horizontally. QR Codes could be scanned both vertically and horizontally, making them two-dimensional. Moreover, they could also retrieve data in case of damage. A revolutionary technology was in the making!
The only thing remaining: finding a pattern that machines could scan fast enough. Hara and team found the winning combination in a square pattern in a unique black-and-white ratio (1:1:3:1:1).
QR Code technology was invented and globally launched by Denso Wave in 1994.
In the 2000s , QR Code use cases mainly were limited to manufacturing. From 2002 to 2011, the role of QR Codes was cemented due to their invaluable aid in handling public emergencies, such as the mad cow disease and the Fukushima nuclear disaster. Ironically, QR Codes would have again proved their worth during another public emergency: the COVID outbreak 2020.
With the rise of smartphones, QR Code usage spread to diverse industries. In fact, it made sharing and receiving information possible anywhere and at any time.
QR Codes became a household technology after 2020. Today, QR Code tools, makers, and generators are widely used to generate QR Codes for several use cases.
Read more: Want to delve deeper? Dig into the history of QR Codes in 10 minutes!
What is the purpose of a QR Code?
While QR Codes started as a necessary invention for immediate emergencies, they connect the physical and digital worlds today.
QR Codes don't get many existential thoughts; they have a solid meaning and purpose. They serve individuals, solopreneurs, startups, and businesses for sharing portfolios, products, and services.
Some of the reasons why QR Codes are an ideal fit for today’s digital landscape are:
- Rise in smartphone use: The number of smartphone users in the US is expected to be around 320 million by 2025. This has paved the way for QR Codes to become a primary marketing and advertising channel.
- Contactless interactions: In a post-pandemic world, QR Codes reduce the need for physical contact and promote digital interactions, such as sharing digital business cards.
- Universal integration: QR Codes can link to any digital entity, such as apps, websites, URLs, social media accounts, payment gateways, and more; the perfect blend of online and offline worlds.
- Adaptability: QR Codes can store a wide variety of information, such as PDFs, text, email, contacts, URLs, images, apps, and more. This way, it can be used across industries, businesses, and use cases.
- Cost-effective marketing: With QR Codes, business owners can easily reach their target audiences without delays or wasteful spending.
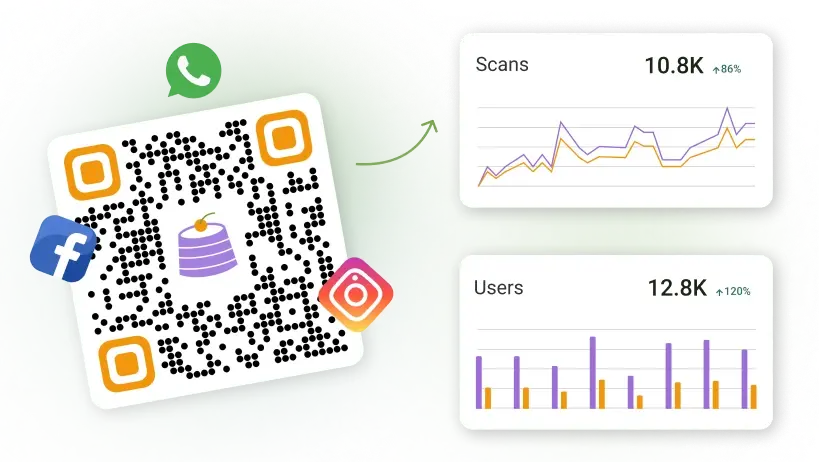
- Data tracking and analytics: With trackable QR Codes, it’s possible to access scan data and gain valuable insights into audience behavior and campaign success.
- Customer service: QR Codes can help customers with quick access to phone or email support and additional resources, such as user manuals, troubleshooting guides, etc.
- Security: QR Codes help protect sensitive information and maintain data privacy with security measures, such as encryption.
What are the different parts of a QR Code?

QR Codes are an evolution in design from barcodes. One-dimensional barcodes are scanned by light from a barcode scanner. Two-dimensional QR Codes are scanned and then processed through sensors (available on all smartphones).
This is possible because of the various elements in a QR Code:
1. Position pattern
Ever noticed the three squares at the corners of any QR Code? They are known as position markers in technical terms and QR Code eyes in simpler terms. The eyes of a QR Code help locate the QR Code, identify its direction, determine its orientation, and scan it fast.
2. Alignment pattern
When you scan a QR Code, the camera focuses on the smaller square at the bottom right of your QR Code pattern. This square helps as a backup position pattern to orient the image. The bigger a QR Code gets, the more alignment patterns it needs for scanning. The alignment pattern is especially needed if the QR Code is printed on a curved surface.
3. Timing pattern
Timing patterns are dots or pixels between two position markers in one corner. They help locate the position markers and read the data matrix to determine the QR Code size.
4. Quiet zone
Have you noticed that the four edges of a QR Code are always left blank? This is intentional and based on the principle of white space in design. This crucial buffer helps a scanner identify the QR Code boundaries.
5. Data and error correction codes
This QR Code section contains two parts: the data and error correction modules. The data modules are the majority of dots or pixels containing data The error correction module enables you to scan a QR Code even if parts of it is damaged.
6. Version information
The version information in a QR Code tells the scanner how much data it contains and which QR Code version it belongs to. Presently, there are 40 versions of QR Codes, with 1 to 7 being the most commonly used. The higher the data, the higher the version code.
7. Format information
Located at the edges of the position patterns, the format information prevents the scanners from being confused and makes the QR Code easy to scan. How? It contains two things: the error correction levels and the mask pattern.
How does a QR Code work?
Knowing its elements makes it easier to understand how a QR Code works.
A QR Code contains three types of data:
- Size This is directly dependent on the QR Code version. A version 1 QR Code (the smallest) contains 21 rows by 21 columns, whereas version 40 (the largest) contains 177 rows by 177 columns
- Error correction levels: These work like a backup of your QR Code data. The higher the error correction level, the greater the chances of retrieving the data after damage to a QR Code. Inversely, the lower the error correction level, the more space for data and size. There are four levels: low, medium, quartile, and high.
- Data type: QR Codes can store four types of data: numeric, alphanumeric, binary/byte, and Kanji/kana. Of these, bytes and kanji are less frequently used. QR Codes are popular since they can contain large amounts of data: 7,089 numeric characters or 2,953 alphanumeric characters versus 20 to 100 characters in bar codes.
Note: If you worry that adding more characters to your QR Code will make it bulky and complex, then don’t because there is a way out. It’s called dynamic QR Codes. They redirect the information to a URL, so your QR Codes don’t store data directly. The result: lighter QR Codes!
This data appears in the form of patterns or pixels in QR Codes. They can represent any type of information: text messages, URLs, videos, and more. This is how you can view any information format when you scan a QR Code.
When you scan a QR Code, the scanner reads this information from the pixels and presents the information in the intended format (PDF, image, contact, app, etc.).
If QR Codes have seemed like a jigsaw puzzle to you to date, hopefully, they will now be full of meaning. The little black-and-white square patterns will seem like chambers holding precious information.
What happens when you scan a QR Code?

Let’s take a peek behind the curtains to understand what happens when you scan a QR Code.
Step 1: Point your phone at a QR Code
Your phone camera gets ready to locate the QR Code.
Step 2: Locate the QR Code
The QR Code scanner on your smartphone identifies the QR Code through the position markers. The quiet zone helps the scanner mark the edges and find the QR Code boundaries.
Step 3: Read the data
The scanner begins reading the data from the bottom right corner. It turns the bits (QR dots or pixels) into different data types (numeric, alphanumeric, byte, or kanji). It moves upwards to the next eight modules and decodes the character count (the total number of characters in the encoded data).
The scanner moves down to up, right to left, and zig-zag multiple times to read the data until it finds the total number of characters.
Finally, it reads the error correction modules to check the amount of data backup available in case of QR Code damage.
Step 4: Translating the data
The phone data processor converts the data into readable information, such as URL, text, app, contact, etc.
Step 5: Present the data
Once the information is decoded, your phone triggers a specific action based on it, such as opening a URL, playing a video, etc. The phone can present the data from the same QR Code (static QR Code) or a redirected code (dynamic QR Code).
It takes 0.1 seconds for your phone to scan a QR Code and 100 milliseconds for the QR Code to redirect you to the required information. So, the entire process takes a handful of seconds.
How to create a QR Code?
If you’re wondering how QR Codes are generated, this section is your go-to.
To create a QR Code, you’ll need a QR Code generator: a tool or software that helps you make QR Codes.
You choose the type of data you want to input (website, app, contact), and the QR Code maker produces a QR Code with that data that anyone can access by scanning the QR Code with their phone.
For example, if you use The QR Code Generator, you can make a QR Code in three steps:
Step 1: Choose your QR Code type
You can select from URL, app, PDF, and other options. At this stage, you can also choose whether to create a static or dynamic QR Code.
Step 2: Input additional details and customize your QR Code
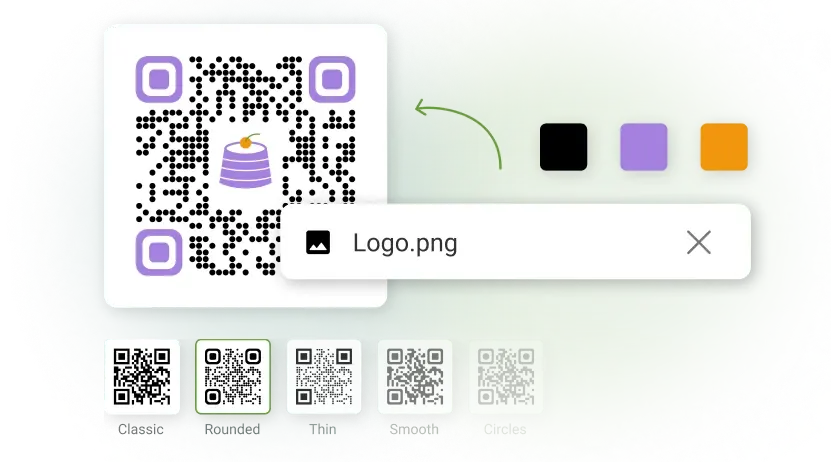
Add the necessary information in the respective fields. Personalize your QR Code according to your preference by customizing the logo, colors, and other aspects.
Step 3: Download your QR Code
Choose the preferred file format based on your use case and download your QR Code.
Are QR Codes safe to use?
If you’re new to QR Codes, it’s natural to be apprehensive about how safe it is to use QR Codes. As a user, you may wonder what type of data QR Codes collect.
Since they are simple to use and easily accessible, they can attract many scams and trap unassuming people.
Some of the common QR Code scams include:
-
Phishing attacks: Emails or messages containing malicious QR Codes that, once scanned, send you to malicious websites. This is also known as quishing.
-
Tampered QR Codes: Scammers replace genuine QR Codes with malicious ones that take you to phishing sites or download malware. This happens especially in public areas, such as restaurants or parking lots.
-
Fake online stores: Fake stores with QR Codes draw you to their websites or trick you into purchasing.
-
Cryptocurrency scams: Cryptocurrency QR Codes can lure you with fake investment opportunities to get payment creds or steal funds.
How to protect yourself from QR Code scams?

What type of data do QR Codes collect?
QR Codes themselves don’t collect data; they simply store and present information. However, the QR Code generator or the redirected site may collect various forms of data.
The data collected by QR Codes is usually non-personal in nature. For example, trackable QR Codes collect user activity patterns to improve campaign effectiveness.
Here are the common data types QR Codes collect:
- Device information: Includes device type (mobile, tablet, etc.), operating system (iOS, Android, etc.), browser type (Chrome, Safari, etc.), IP address
- User information: Name, email address, phone number, location, demographic information (age, gender, etc.)
- User activity data: Time and date of scan, pages visited, actions taken (purchases, video views, etc.)
What are the different types of QR Codes?
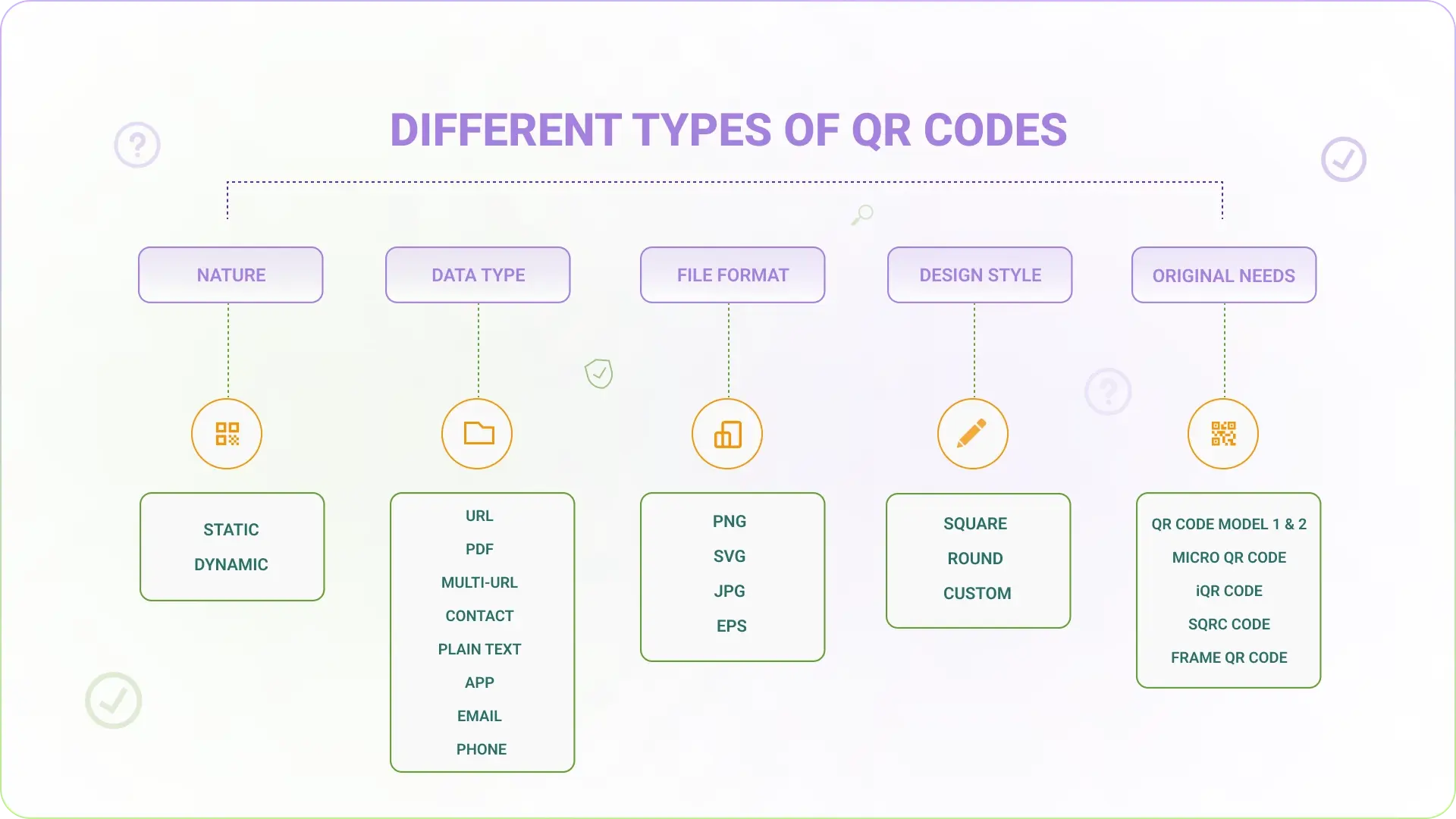
You must have heard different QR Code names floating around: static, dynamic, circle, SVG, micro, etc.
Let’s demystify each type of QR Code.
By nature
By nature, QR Codes can be static or dynamic.
-
Static QR Code: A static QR Code is a type of QR Code that can’t be edited or changed once created. The data it contains is directly embedded in its pattern. If you need to update the data, you’ll need to create a new QR Code.
Static QR Codes are non-editable and non-trackable but light-weight and ideal for one-time small campaigns.
-
Dynamic QR Code: A dynamic QR Code is a type of QR Code that can be edited or updated, even after it’s generated. Dynamic QR Codes link the data to a short URL that redirects to a website or landing page and does not contain it in the pattern like static QR Codes. This means you can change the QR Code destination URL without having to reprint the QR Code.
Dynamic QR Codes are editable and trackable, contain more data, and are ideal for complex and big campaigns.
By data type
-
URL QR Code: Redirects users to a specific website
-
PDF QR Code: Embeds a PDF
-
Multi-URL QR Code: Directs users to a webpage with multiple links
-
Contact QR Code: Stores contact information (name, phone number, email address, etc.)
-
Plain text QR Code: Encodes plain text messages
-
App QR Code: Directs users to app download pages
-
SMS QR Code: Pre-fills SMSs
-
Email QR Code: Pre-fills email addresses and subject lines
-
Phone QR Code: Encodes a phone number
By file format
-
PNG QR Code: Lossless compression, widely supported, ideal for QR Codes for different surfaces and resolutions
-
SVG QR Code: Vector-based format, high-quality, resizeable QR Codes, ideal for printing and displays
-
JPG QR Code: Lossy compression, small file size and image quality, ideal for digital campaigns and online sharing
-
EPS QR Code: Vector-based, ideal for professional printing and design, needs special software to run
By design style
-
Square QR Code: The classic shape used in most QR Code applications ensures optimum scannability and data capacity
-
Round QR Code: A modern variation ideal for branding and creative designs, can have low scanning accuracy
-
Custom styles: Custom designs, such as logos or objects ideal for marketing and branding campaigns, with high customization potential but limited scannability
By original needs
-
QR Code Model 1 & 2: QR Code Model 1 is an outdated version (73x73) that can store 1,167 numerals. QR Code Model 2 is an updated version of Model 1 with 177x177 modules and a storage capacity of 7,089 numerals. Both are ideal for use in restaurants and retail shops.
-
Micro QR Code: This unique QR Code can work with only one position marking pattern. This makes it possible to produce QR Codes with smaller printing areas. There are four variants (M1 to M4), starting from 2 to 17 modules. They contain 35 numerals and can be ideal for websites and business cards.
-
iQR Code: The characteristic of this two-dimensional QR Code is that it reads and stores large amounts of data (80% more than regular QR Codes). It has a storage capacity of 40,000 numerals and an error correction capacity of 50%. Due to its square or rectangular shape, it can be printed in narrow spaces while containing more data.
-
SQRC Code: This QR Code has two sections—public and private. Both sections contain different types of data and control levels. It looks exactly like traditional QR Codes and has similar error correction levels. It’s ideal for handling both external and internal company data.
-
Frame QR Code: Just like its name, this QR Code contains a ‘canvas area’ where you can store images or text. Since the frame is customizable, it can be used for various situations.
Advantages of using QR Codes
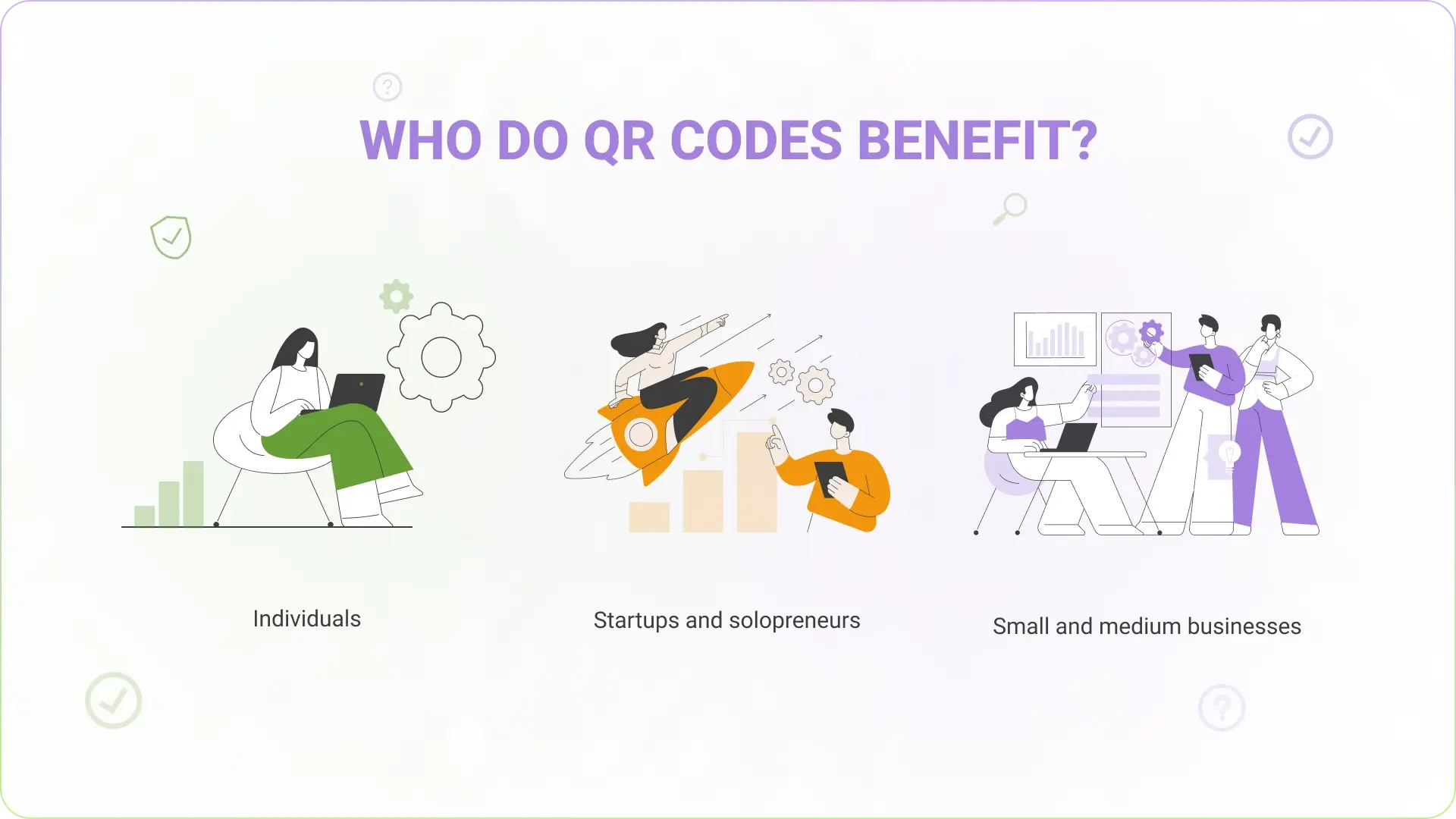
Depending on what use case you have, QR Codes can help you in different ways:
For individuals
Looking for quick ways to store and share portfolios or information? QR Codes offer helpful solutions:
-
Fast sharing: Share contact details, social media profiles, websites, or portfolios effortlessly
-
Secure storage: Store essential documents or medical information in a secure, ready-to-share digital format
For startups and solopreneurs
Small budgets, more focused marketing efforts, and organizing operations: what most solopreneurs and startups struggle with.
Here’s how QR Codes can help:
-
Cost-effective solution: QR Codes don’t require huge budgets and easily integrate with existing software. With tools like The QR Code Generator, you can create a QR Code in three steps.
-
More eyeballs: Catch a slightly high-hanging fruit with a lower budget. Customizable QR Codes get you more visibility in a world with shrinking attention spans.
For small and medium businesses
Running a business means running after ROI and chasing the best customer experience. QR Codes can make a difference here:
-
Targeted marketing: Trackable QR Codes help you figure out what happens after a QR Code scan: how many users scan, what their demographics are, which device they use, etc.
-
Superior experiences: QR Codes can help offer personalized experiences to customers and make sharing product information and feedback easy.
Creative uses of QR Codes
“With traditional media, like a billboard or TV, you can estimate how many people may have seen it, but you don’t know how people actually interacted with it. With QR Codes, we can get reporting on those scans.”, says Sarah Cucchiara, a senior vice president at BrandMuscle, which uses a QR Code menu.
Here are 5 industries where QR Codes can make a difference:
Retail
You can use QR Codes for your thrift store, boutique, or retail outlet. Here are some creative uses:
-
Share product information with customers: Let visitors scan a QR Code to check food ingredients, usage guides, new launches, and more.
-
Make product packaging interactive: Use QR Codes for your packaging to redirect users to videos or exclusive discounts
-
Create an exciting in-store experience: Make your products larger than life with in-store virtual experiences; make the purchase process faster with QR Code payments
Education
QR Codes pave the way for smarter classrooms and more immersive learning experiences. Here’s how:
-
Add interactive elements in learning materials: Make learning fun by adding a QR Code in textbooks linking to videos, quizzes, or additional resources.
-
Collect student feedback with QR Codes: Want to optimize your teaching approach? Let students scan a QR Code to share their feedback or suggestions.
-
Track attendance with QR Codes: To save time and effort, let students mark attendance with a QR Code scan.
Marketing and advertising
Elevate your marketing and advertising campaigns with QR Codes. Try out these ideas:
-
Get more visibility for your brand: Create social media QR Codes to attract more followers and eyeballs to your content.
-
Add QR Codes to your marketing materials: Prospects take faster action when you add QR Codes on marketing materials, such as brochures, posters, flyers, or billboards.
-
Track QR Codes to optimize your campaigns: Learn more about your customers and how they engage with your campaign with QR Code scan tracking.
Real estate
Make property hunting easy for clients and drive more leads for your real estate business.
Try out these QR Code hacks:
-
Offer virtual property tours: Let users scan a QR Code to enable 360-degree property views and video walkthroughs.
-
Share property information: Prospects can view floor plans, pricing, and agent contacts quickly with QR Codes.
-
Automate open house registration: Make open house registration easy with QR Codes.
Hospitality
Hotels and restaurants have plenty of use cases with QR Codes. Here are a few:
-
Make hotel check-ins easy: Offer speedy and personalized check-ins to customers with QR Codes.
-
Make menu viewing and ordering simple: Digital menus are quicker for customers to check the items and order.
-
Sharing information: Customers can get event information, schedules, maps, or recipes with a QR Code scan.
Frequently asked questions
1. What is QR full form?
The full form of QR Code is a Quick Response Code.
2. Are QR Codes free?
It can be free or paid, depending on which tool or generator you’re using to create your QR Codes. Most QR Code tools have both free and paid plans. There are some tools, such as The QR Code Generator, which are forever free.
3. Do QR Codes require Internet?
Offline QR Codes don’t require the internet. If you create an offline QR Code, such as a text, contact number, or Wi-Fi, users can open it without any internet connection. However, an online QR Code, such as a website URL, will need an Internet connection to open it.
4. Do QR Codes expire?
QR Codes expire when they are damaged. If it’s a static QR Code, it will expire after a specific use case. If it’s a dynamic QR Code, will expire based on the plan details of the QR Code generator tool.
5. Are QR Codes always black and white?
No, you can customize your QR Code colors based on your preference. Many QR Code generators offer the option to customize your QR Code.
6. What is the difference between QR Codes and barcodes?
There are several differences between QR Codes and barcodes:
-
QR Codes are two-dimensional codes, whereas barcodes are one-dimensional codes
-
QR Codes read data both vertically and horizontally; barcodes read data only horizontally
-
QR Codes can store different kinds of data, whereas barcodes can store only numeric and alphanumeric data
-
QR Codes can store up to 3,000 characters, whereas barcodes can store up to 15-20 characters
-
QR Codes can be scanned by any mobile device, whereas barcodes need to be scanned with special barcode scanners
-
QR Codes offer extensive customization, whereas barcodes offer only limited customization